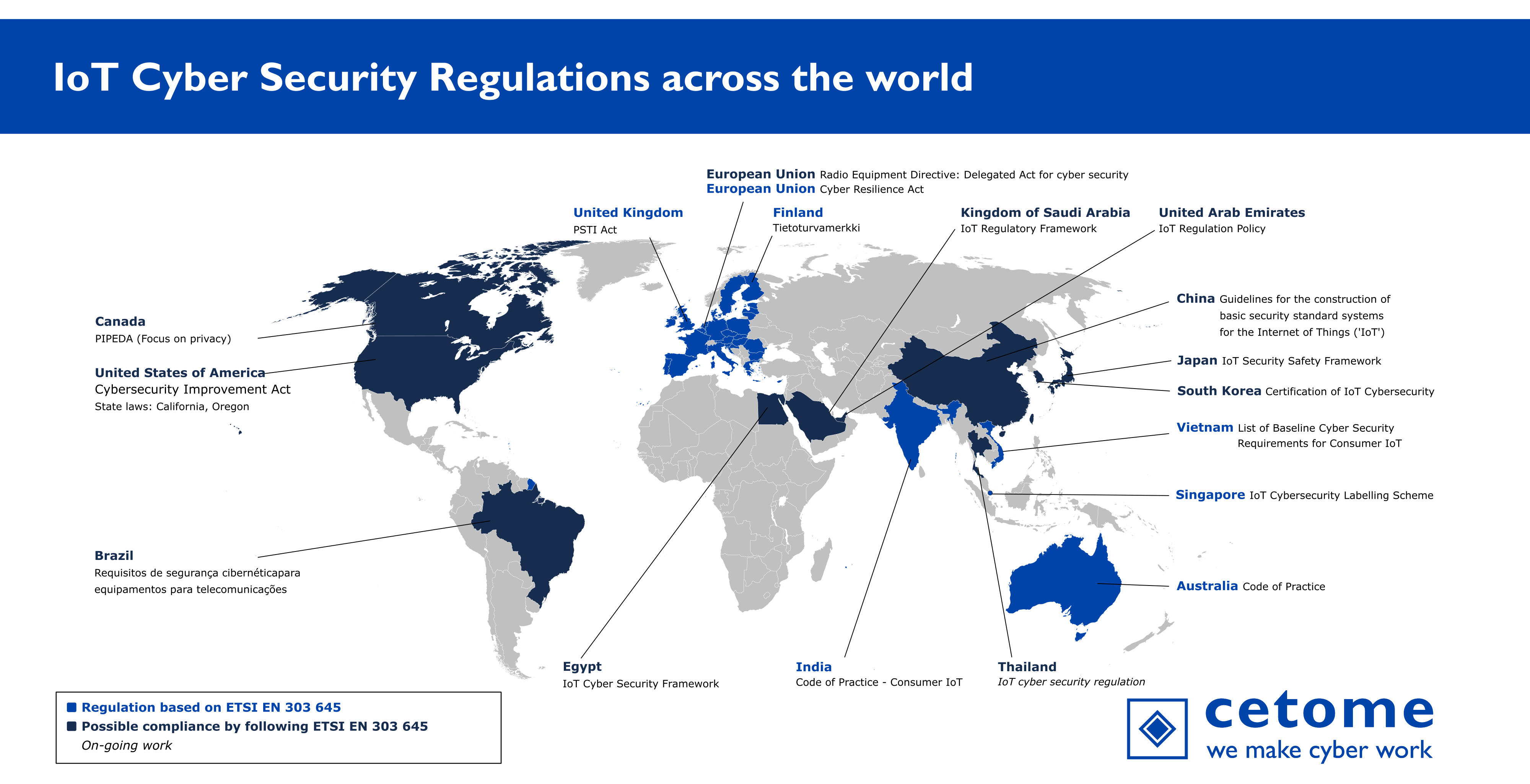
This panorama presents the list of regulations across the world. Most information was collected through public means.
Countries with Regulations
Current countries and zones with IoT cyber security regulations:
Australia
Brazil
Canada
China
Egypt
European Union
Finland
Hungary
India
Japan
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Singapore
South Korea
Sultanate of Oman
Thailand Preliminary work announced. More information needed.
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States of America
Vietnam
If you want to reference this work, please refer to this page directly. This is to limit forks and consolidate efforts.
Note: The data is available on GitHub if you want to generate your own panorama.
For citations, please use: cetome, Panorama of IoT Cyber Security Regulations Across the World. https://cetome.com/panorama
Map of IoT Cyber Security Regulations
Summary table
The table below presents the results of our analysis with the following indicators:
- ✅ Yes, 🆗 Partially, ❌ No and 🛑 N/A (Not Applicable) when the information is available.
- ❔ TBC (To Be Confirmed) when no information is available due to an on-going development.
| Name of the regulation | Cyber Security (Security Standards for Smart Devices) Rules 2025 | Requisitos de segurança cibernética para equipamentos para telecomunicações | Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act | Guidelines for the Construction of IoT Basic Security Standard Systems (2021 Edition) | EG-CSEC-OPER 100-01 DATABASE POLICY-2210-EN | Cyber Resilience Act (EU 2024/2847) | Articles 3(3)(e) and (f) of the Radio Equipment Directive 2014/53/EU | Tietoturvamerkki | Decree No. 10/2024. (VIII. 8.) of the Supreme Administrative Court on the national cybersecurity certification system for IoT devices | Code of Practice for Securing Consumer Internet of Things (IoT) | IoT Security Safety Framework | Internet of Things Regulatory Framework | Internet of Things Security Regulatory Framework | Cybersecurity labelling scheme | Certification of IoT Cybersecurity | IoT cyber security regulations | Internet of Things Regulatory Policy | The Product Security and Telecommunications Infrastructure Regulations | H.R. 1668 - IoT Cybersecurity Improvement Act of 2020 | Senate Bill No. 327 - Information privacy: connected devices | House Bill 2395 | Decision No. 736/QĐ-BTTTT on 31 May 2021 ("Decision") Setting out the List of Baseline Requirements to Ensure Cyber Security for Consumer IoT Devices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shortname | Security Standards for Smart Devices | Act nº 77, 5th of January 2021 | PIPEDA | IoT BSSS | IoT Cyber Security Framework | CRA | RED | Finnish Cybersecurity Label | IoT cybersecurity certification | Code of Practice - Consumer IoT | IoT-SSF | IoT Regulatory Framework | IoT SRF | CSL | CIC | 🛑 N/A | IoT Regulatory Policy | PSTI | IoT Cybersecurity Improvement Act of 2020 | SB-327 | HB 2395 | List of Baseline Cyber Security Requirements for Consumer IoT |
| Author | Australian Government, Department of Home Affairs | Brazilian Agency of Telecommunications (Anatel) | Office of the Privacy Commissioner of Canada | Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) | Egypt | European Commission | European Commission | Finnish transport and communication agency (Traficom) | Supervisory Authority for Regulatory Affairs of Hungary (SZFTH) | Telecommunication Engineering Center | Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) | Communication and Information Technology Commission | Telecommunications Regulatory Authority | Cyber Security Agency of Singapore (CSA) | Korea Internet & Security Agency (KISA) | Office of the National Broadcasting and Telecommunications Commission (NBTC) | Telecommunications Regulatory Authority | Department for Digital, Media, Culture and Science | Congress | California State Senate | Oregon House of Representatives | Authority of Information Security (AIS) |
| URL | Source | Source | Source | Source | Source | Source | Source | Source | Source | Source | Source | Source | Source | Source | Source | 🛑 N/A | Source | Source | Source | Source | Source | Source |
| Date of issue | March 2025 | 5 January 2021 | August 2020 | 23 September 2021 | October 2022 | 23 October 2024 | 29 October 2021 | 2020 | October 2024 | 31/08/2021 | 5 November 2020 | September 2019 | 14 December 2021 | October 2020 | 2 December 2022 | On-going work | 22 March 2018 | 24/11/2021 | 12 April 2020 | 28 September 2018 | 16 April 2019 | 31/05/2021 |
| Is the regulation in force? | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Scope | Internet-connectable products | IoT and telecommunication equipment | All IoT systems (privacy-focused) | All IoT systems | IoT products and services | Products with a digital element | Childcare radio equipment, toys, wearable devices, Internet-connected radio equipment (with exceptionsy) | Consumer IoT | IoT devices | Consumer IoT | All IoT devices and systems | All IoT systems | All IoT systems | Consumer IoT | IoT systems | ❔ TBC | Radio and Telecommunications Terminal Equipment providing IoT Service, IoT service providers | Consumer IoT | All IoT devices and systems | Consumer IoT | Consumer IoT | Consumer IoT |
| Target Actors | IoT manufacturers and suppliers | IoT manufacturers, IoT suppliers | IoT manufacturers | IoT manufacturers | IoT manufacturers, IoT service providers | Manufacturers, importers, distributors, commercial open source | IoT manufacturers | IoT manufacturers | IoT manufacturers | IoT Device Manufacturers, IoT Service Providers / System integrators, Mobile Application Developers, Retailers | IoT manufacturers | IoT manufacturers, IoT service providers | Vendors, Service Providers, Integrators, Licensees | IoT manufacturers, Consumers | IoT manufacturers | ❔ TBC | IoT manufacturers, IoT service providers | IoT manufacturers (producers), distributors, importers | Federal agencies owning or controlling IoT devices and systems | IoT manufacturers | IoT manufacturers | IoT manufacturers |
| Mandatory or Voluntary? | Mandatory | Mandatory | Mandatory | Mandatory | Voluntary | Mandatory | Mandatory | Voluntary | Mandatory | Voluntary | Voluntary | Mandatory | Mix of mandatory and voluntary controls | Voluntary | Voluntary | Mandatory (❔ TBC) | Mandatory | Mandatory | Mandatory | Mandatory | Mandatory | Voluntary |
| Is there a label or a certification? | ❌ No | ✅ Certification (homologation) | ❌ No | ✅ Certification | ❌ No | ✅ Future hEN | ❌ No | ✅ Label | ✅ Label | ✅ Certification | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Label (levels 1 and 2), ✅ Certification (levels 3 and 4) | ✅ | ❔ TBC | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No |
| Does the regulation mandate baseline security requirements? | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❔ TBC | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Are there additional requirements to the baseline security? | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | 🛑 N/A | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❔ TBC | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No |
| Does the regulation contains assurance levels? | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | 🛑 N/A | ❌ No | ❔ TBC (possible compliance check for mandatory controls) | ✅ Yes, 4 levels (self-assessment to third-party verification by an accredited lab) | ✅ Yes | ❔ TBC | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No |
| Is compliance with ETSI EN 303 645 a requirement? | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | 🆗 Partially | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ❔ TBC | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (subset) | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Can ETSI EN 303 645 be used to comply with the regulation? | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❔ TBC | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | 🆗 Partially | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Are other standards or guidance referenced? (cf. regulation) | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❔ TBC | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No |
About cetome
cetome is an independent security consultancy based in London, UK and Lyon, France and operating globally. We work with organisations where security is important and that need to tackle several challenges in terms of resources, capabilities or skills. At cetome, we understand the challenges of IoT security and its complexity. We work with IoT manufacturers, service providers and users of consumer and industrial IoT systems to protect these solutions from cyber threats. Our experts make sure that your activity is secure against cyber risks by implementing accepted security measures and help you prepare to future certification.
About the Author
Dr. Cédric LÉVY-BENCHETON is the CEO and founder of cetome. Cédric has expertise in IoT security. He previously worked at ENISA, the European Union Cyber Security Agency.